Preventive Treatments
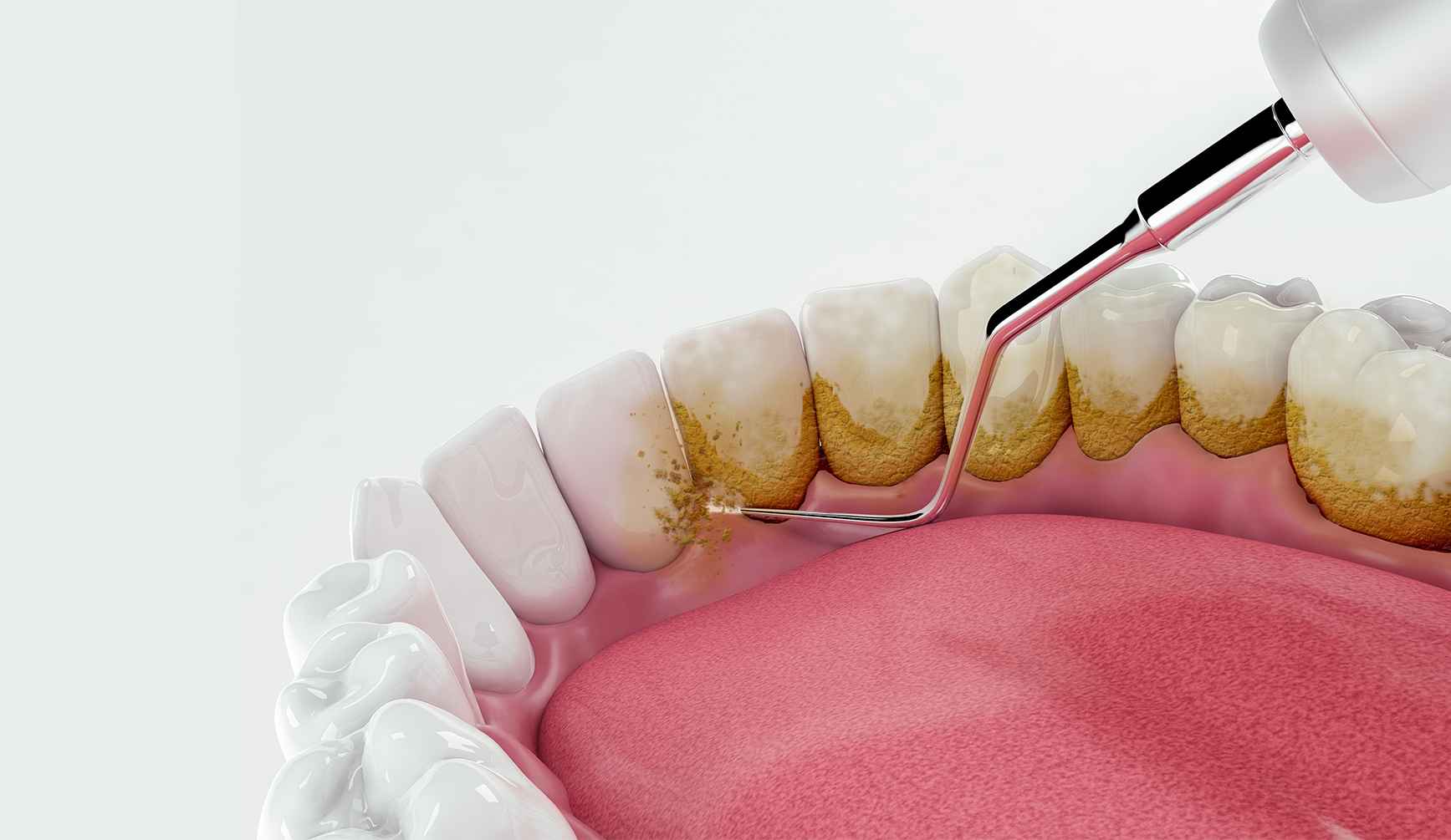
A. Dental Cleaning (Prophylaxis)
-
Problem Addressed: Plaque and tartar buildup, which can lead to cavities or gum irritation.

-
How to Check: Look for yellow or brown buildup on teeth, bad breath that doesn’t go away, or red/swollen gums. A dentist can confirm with a visual exam.

-
Specialist: General Dentist

-
Home Care Tips: Brush twice daily with a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste and floss once daily.

-
Milestone: First cleaning recommended by age 1 or within 6 months of the first tooth.

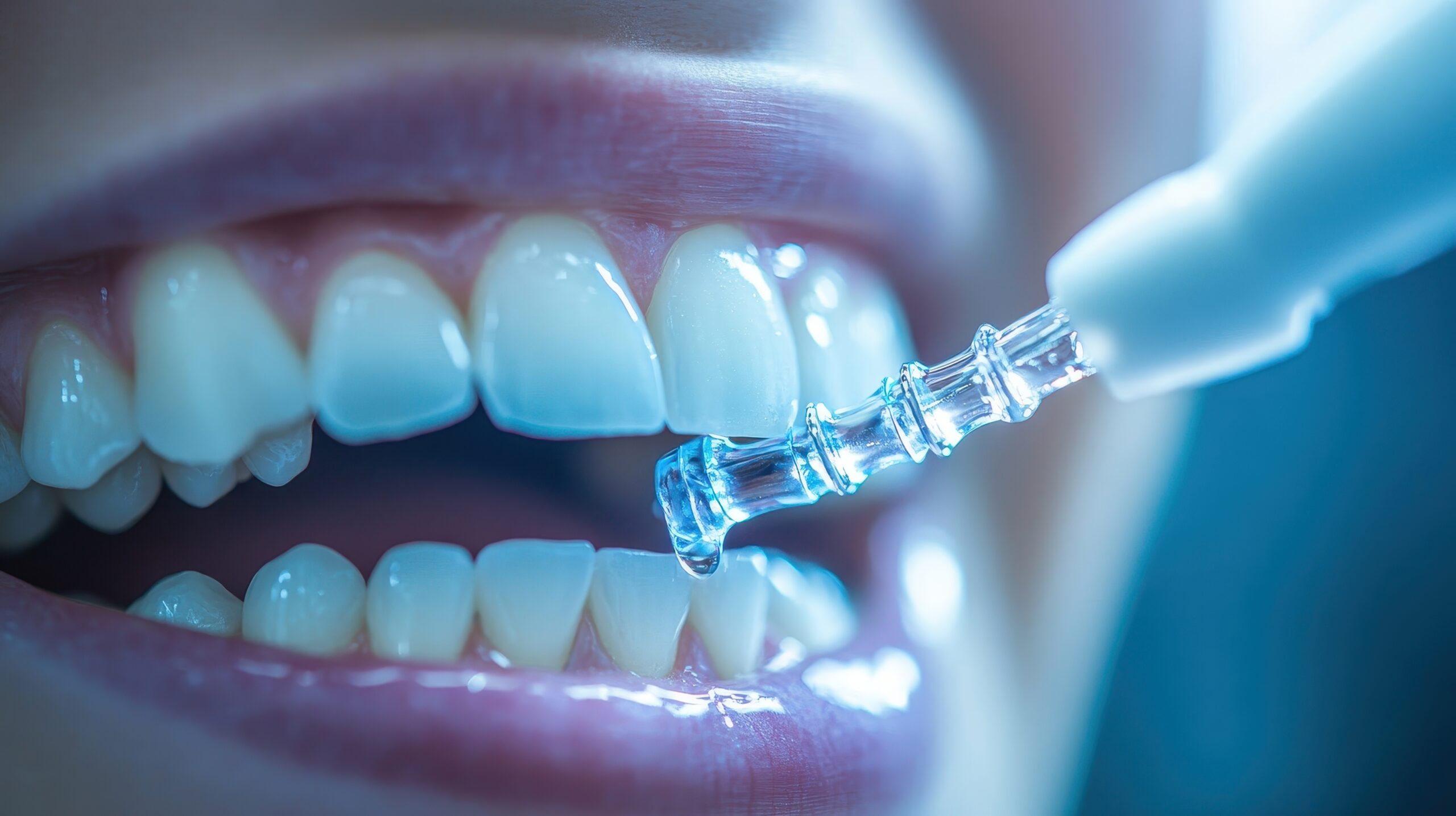
B. Fluoride Applications
-
Problem Addressed: Weak enamel prone to cavities, especially if your child eats sugary snacks or drinks.

-
How to Check: Notice frequent cavities despite good brushing, or ask your dentist to test enamel strength.

-
Specialist: General Dentist or Pediatric Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Limit sugary drinks and use fluoride mouthwash (age 6+) as directed.

-
Milestone: Start around age 2 if cavity risk is high.

C. Pit and Fissure Sealants
-
Problem Addressed: Deep grooves in molars that trap food and cause cavities.

-
How to Check: Look for dark spots or pits in the chewing surfaces of back teeth; a dentist can use a magnifying tool to assess.

-
Specialist: General Dentist or Pediatric Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Encourage chewing sugar-free gum to stimulate saliva, which protects teeth.

-
Milestone: Apply when first molars erupt (around age 6).

D. Anticipatory Guidance for Teething & Oral Habits
-
Problem Addressed: Painful teething, thumb-sucking, or pacifier use that might misalign teeth.

-
How to Check: Watch for excessive drooling, irritability during teething, or thumb-sucking past age 4. A dentist can evaluate jaw alignment.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist or Orthodontist (for habits affecting alignment).

-
Home Care Tip: Offer teething rings for infants and gently discourage thumb-sucking with positive reinforcement.

-
Milestone: Teething begins around 6 months; stop pacifier by age 3.


Restorative Treatments
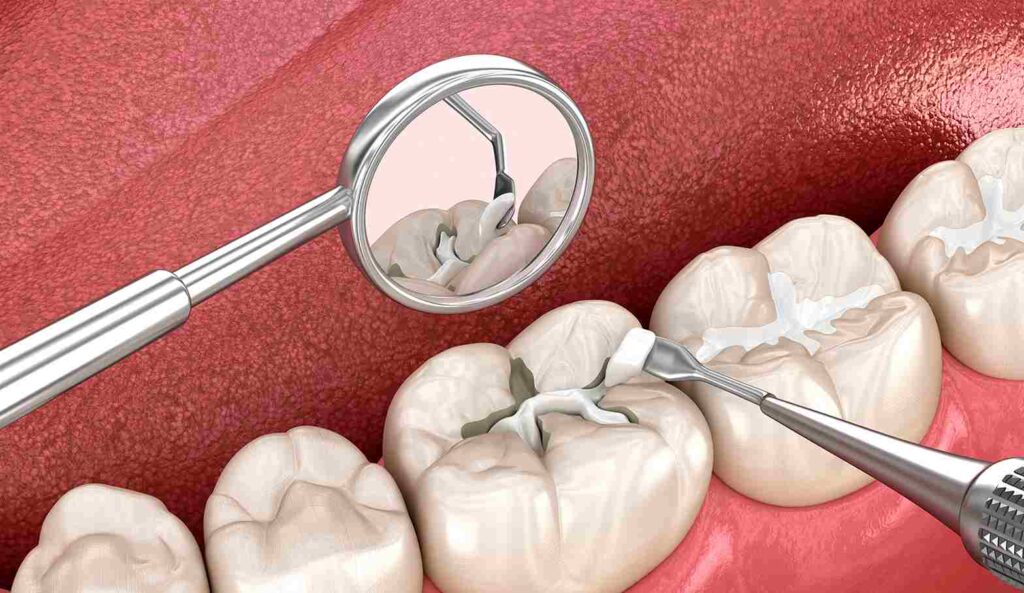
A. Tooth-Colored Fillings (Composite/Glass Ionomer)
-
Problem Addressed: Cavities or small holes in teeth from decay.

-
How to Check: Look for black, brown, or white spots on teeth, or if your child complains of tooth sensitivity/pain. A dentist uses X-rays to confirm.

-
Specialist: General Dentist or Pediatric Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Avoid hard foods (e.g., candy) that can worsen damage.

-
Milestone: Common between ages 2–6 as baby teeth are prone to decay.

B. Stainless Steel Crowns (SSCs)
-
Problem Addressed: Large cavities or broken teeth that can’t be fixed with fillings.

-
How to Check: Notice a tooth with a big hole or crack; your child may wince when eating. Dentist will assess with an exam.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Ensure soft diet post-procedure and monitor for discomfort.

-
Milestone: Typically needed between ages 3–8 for severe decay.
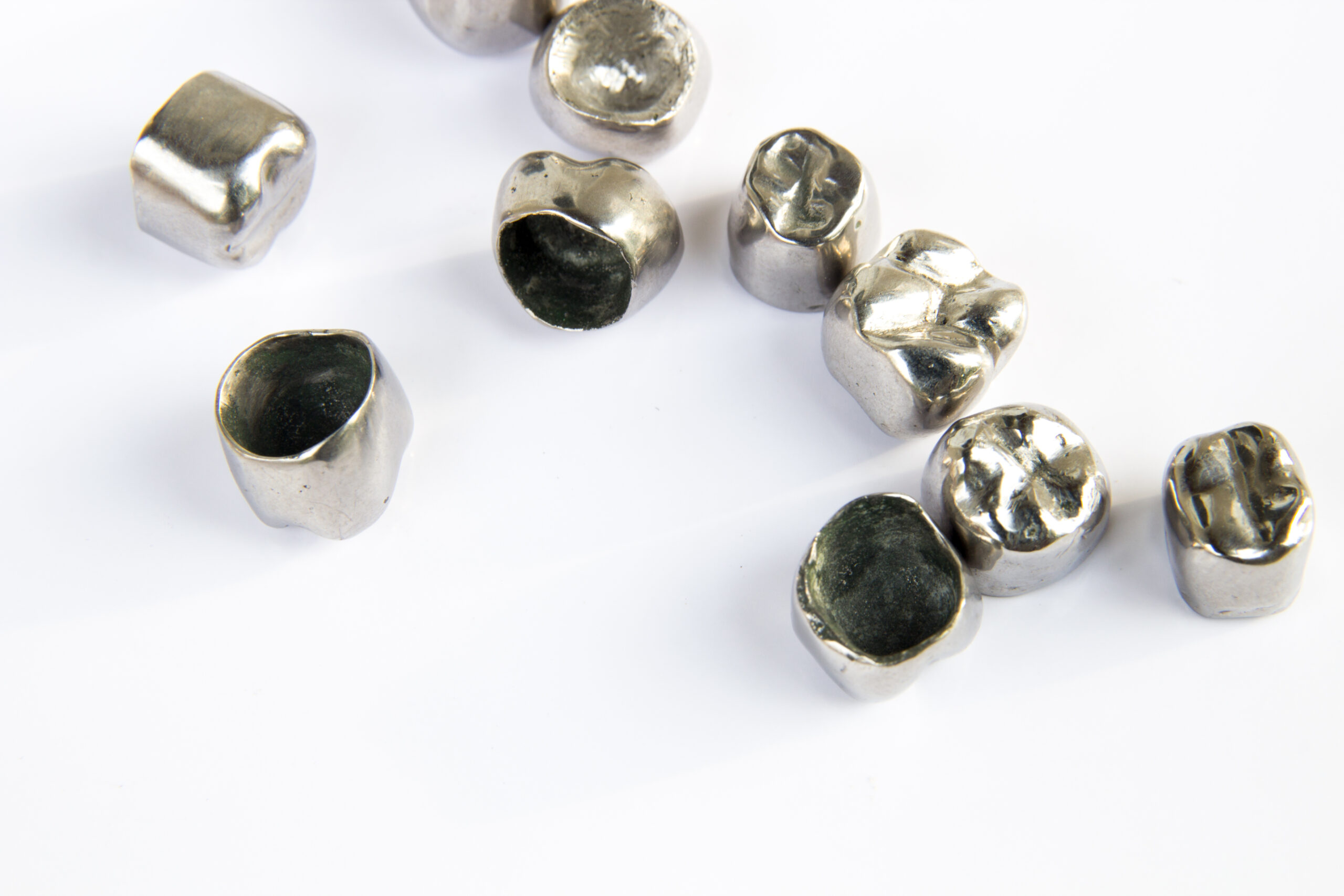


C. Zirconia Crowns (for esthetic needs)
-
Problem Addressed: Damaged front teeth needing a natural look (e.g., after trauma).

-
How to Check: Visible chips or discoloration in front teeth; dentist can evaluate damage.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist or Cosmetic Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Use a mouthguard for sports to prevent further damage.

-
Milestone: Common after age 3 if front teeth are affected.

D. Pulp Therapy: Pulpotomy (for reversible pulpitis), Pulpectomy (for non-vital teeth)
-
Problem Addressed: Infection or inflammation in the tooth’s nerve due to deep decay.

-
How to Check: Severe toothache, swelling, or sensitivity to hot/cold; dentist uses X-rays to diagnose.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist or Endodontist.

-
Home Care Tip: Give pain relief (as advised) and avoid chewing on that side.

-
Milestone: Peaks between ages 3–7 with baby teeth.

E. Space Maintainers: Fixed (band and loop, distal shoe), Removable (Acrylic-based)
-
Problem Addressed: Early tooth loss (e.g., from decay) causing misalignment of permanent teeth.

-
How to Check: Missing baby teeth with no new tooth growing in; dentist can measure gaps.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist or Orthodontist.

-
Home Care Tip: Clean around the device daily to prevent plaque buildup.

-
Milestone: Needed between ages 4–10 if a tooth is lost early.

F. Strip Crowns (for anterior teeth)
-
Problem Addressed: Decayed or damaged front teeth needing a natural appearance.

-
How to Check: Visible decay or chips in front teeth; dentist will assess.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Avoid sticky foods that could dislodge the crown.

-
Milestone: Common between ages 2–6 for front baby teeth.

Orthodontic / Interceptive Treatments
A. Thumb Sucking/Tongue Thrust Appliances
-
Problem Addressed: Persistent thumb-sucking or tongue thrusting causing bite issues.

-
How to Check: Notice teeth misalignment (e.g., open bite) or thumb-sucking past age 5; dentist can evaluate.

-
Specialist: Orthodontist.

-
Home Care Tip: Use positive reinforcement and consult a therapist if needed.

-
Milestone: Address by age 6 before permanent teeth settle.


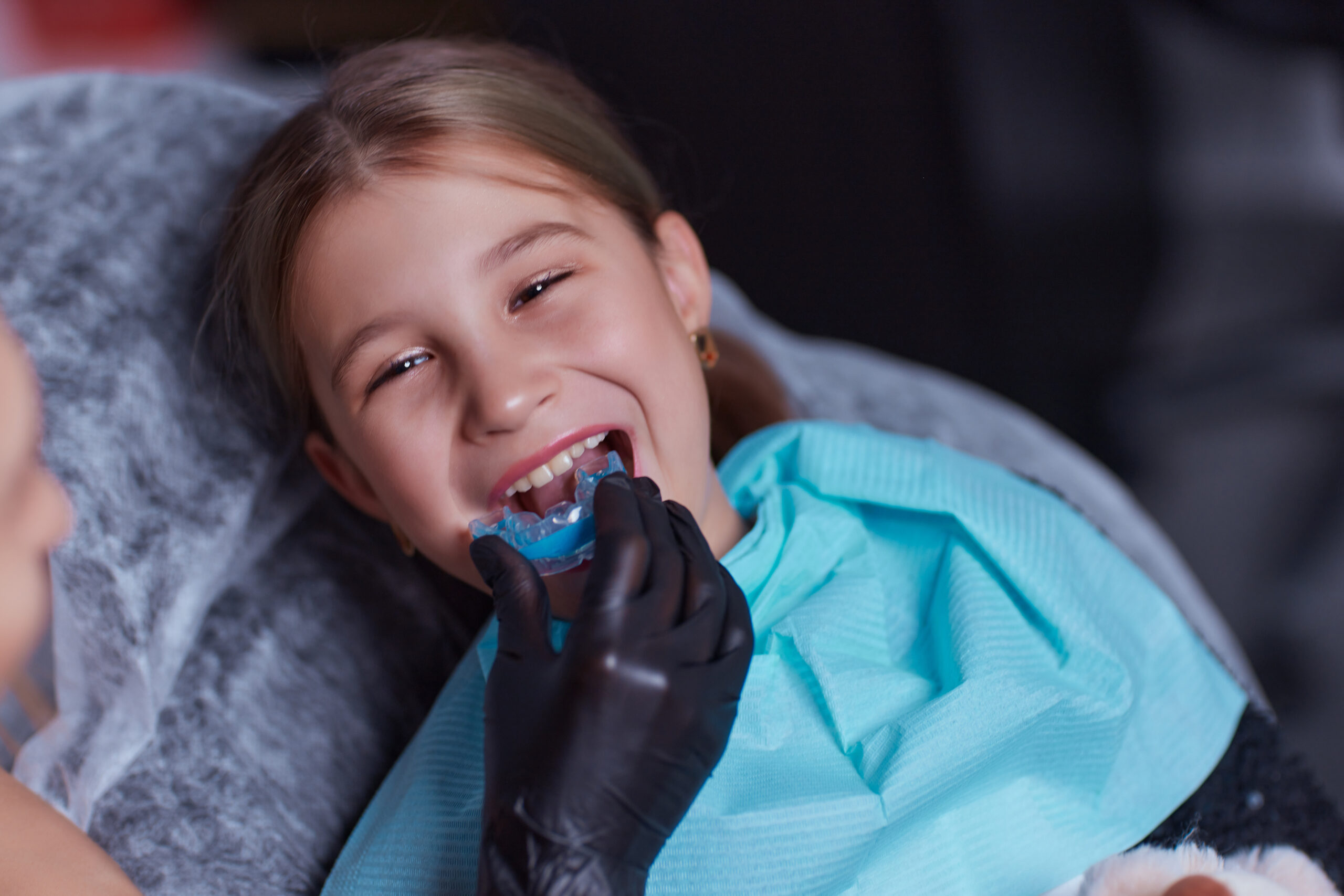
B. Mouth Breathing Correction Appliances
-
Problem Addressed: Chronic mouth breathing (e.g., due to allergies) affecting jaw growth.

-
How to Check: Dry lips, snoring, or a narrow jaw; a dentist or ENT can assess.

-
Specialist: Orthodontist or ENT.

-
Home Care Tip: Use a humidifier and treat allergies with a doctor.

-
Milestone: Monitor by age 5–7 during jaw development.


C. Space Regainers
-
Problem Addressed: Damaged front teeth needing a natural look (e.g., after trauma).

-
How to Check: Crowded or shifted teeth; dentist uses X-rays to confirm.

-
Specialist: Orthodontist.

-
Home Care Tip: Ensure proper cleaning around the device.

-
Milestone: Needed between ages 6–10.

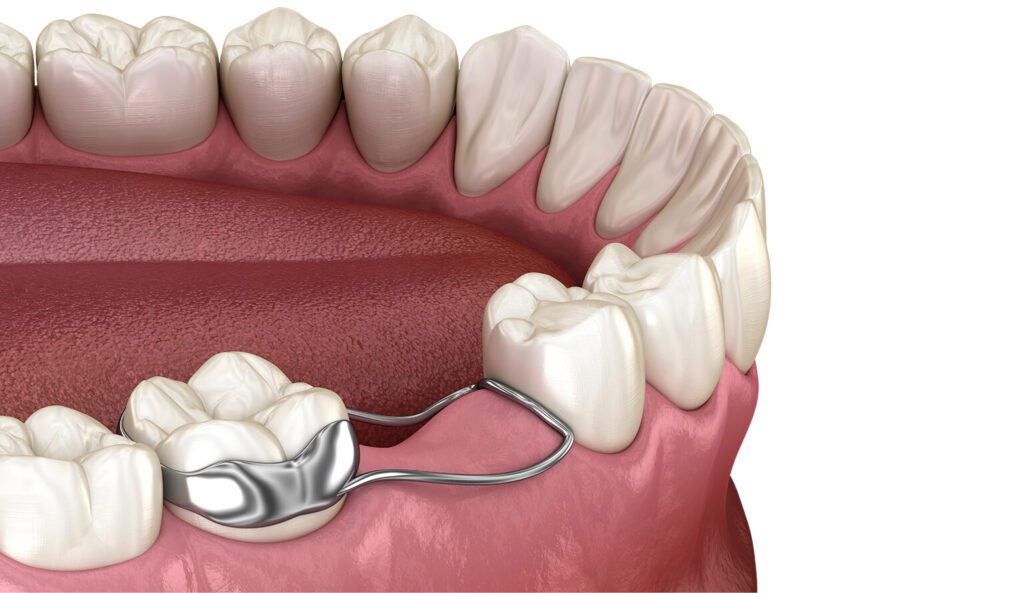
D. Serial Extraction Planning
-
Problem Addressed: Overcrowded teeth needing guided removal to make space.

-
How to Check: Very crowded teeth or jaw; dentist or orthodontist will plan with X-rays.

-
Specialist: Orthodontist.

-
Home Care Tip: Follow post-extraction care instructions closely.

-
Milestone: Planned around ages 7–11.


E. Myofunctional Therapy (for early habits)
-
Problem Addressed: Oral habits (e.g., tongue thrusting) affecting speech or alignment.

-
How to Check: Speech issues or bite problems; specialist will assess.

-
Specialist: Orthodontist or Speech Therapist.

-
Home Care Tip: Practice exercises recommended by the therapist.

-
Milestone: Start by age 5–7 if habits persist.
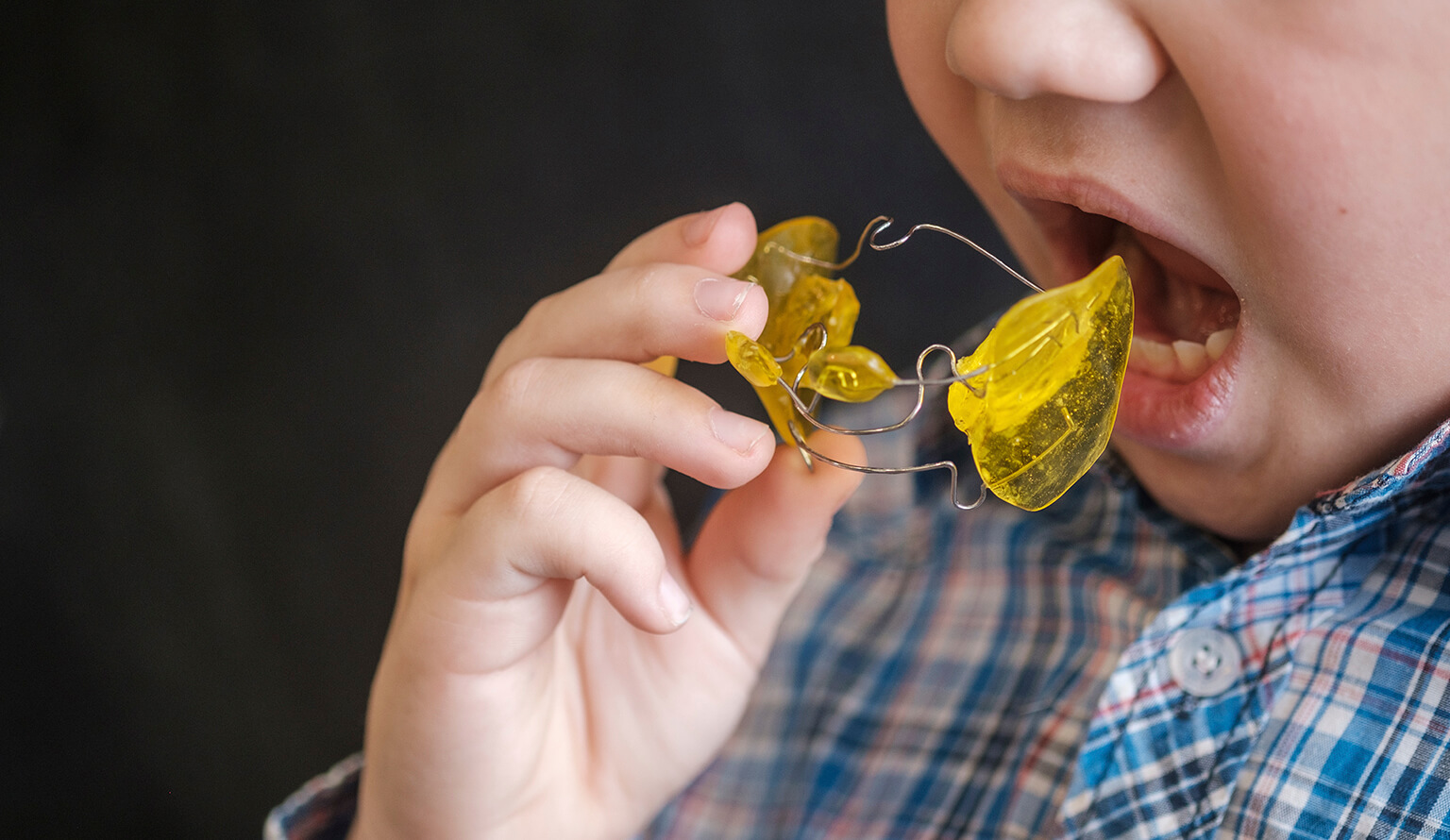


F. Palatal Expanders (in specific cases)
-
Problem Addressed: Narrow upper jaw causing crossbite or crowding.

-
How to Check: Misaligned bite or narrow palate; dentist can measure.

-
Specialist: Orthodontist.

-
Home Care Tip: Turn the expander as instructed and monitor for discomfort.

-
Milestone: Used between ages 6–10 during jaw growth.

Specialized / Other Treatments
A. Tooth Extractions (due to infection or over-retention)
-
Problem Addressed: Severe decay, infection, or baby teeth not falling out.

-
How to Check: Swelling, pain, or a loose tooth that won’t fall; dentist uses X-rays.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist or Oral Surgeon.

-
Home Care Tip: Apply ice and follow soft diet post-extraction.

-
Milestone: Common between ages 6–12.


B. Management of Natal/Neonatal Teeth
-
Problem Addressed: Teeth present at birth or shortly after, which may cause feeding issues.

-
How to Check: Visible teeth in a newborn; consult a dentist.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Monitor feeding and consult a lactation specialist if needed.

-
Milestone: Occurs at birth or within first 3 months.


C. Treatment of Early Childhood Caries (ECC)
-
Problem Addressed: Widespread cavities in very young children, often from bottle-feeding.

-
How to Check: Multiple decayed teeth, especially in toddlers; dentist will examine.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Stop bottle at bedtime and use water instead of juice/milk.

-
Milestone: Peaks between ages 1–4.

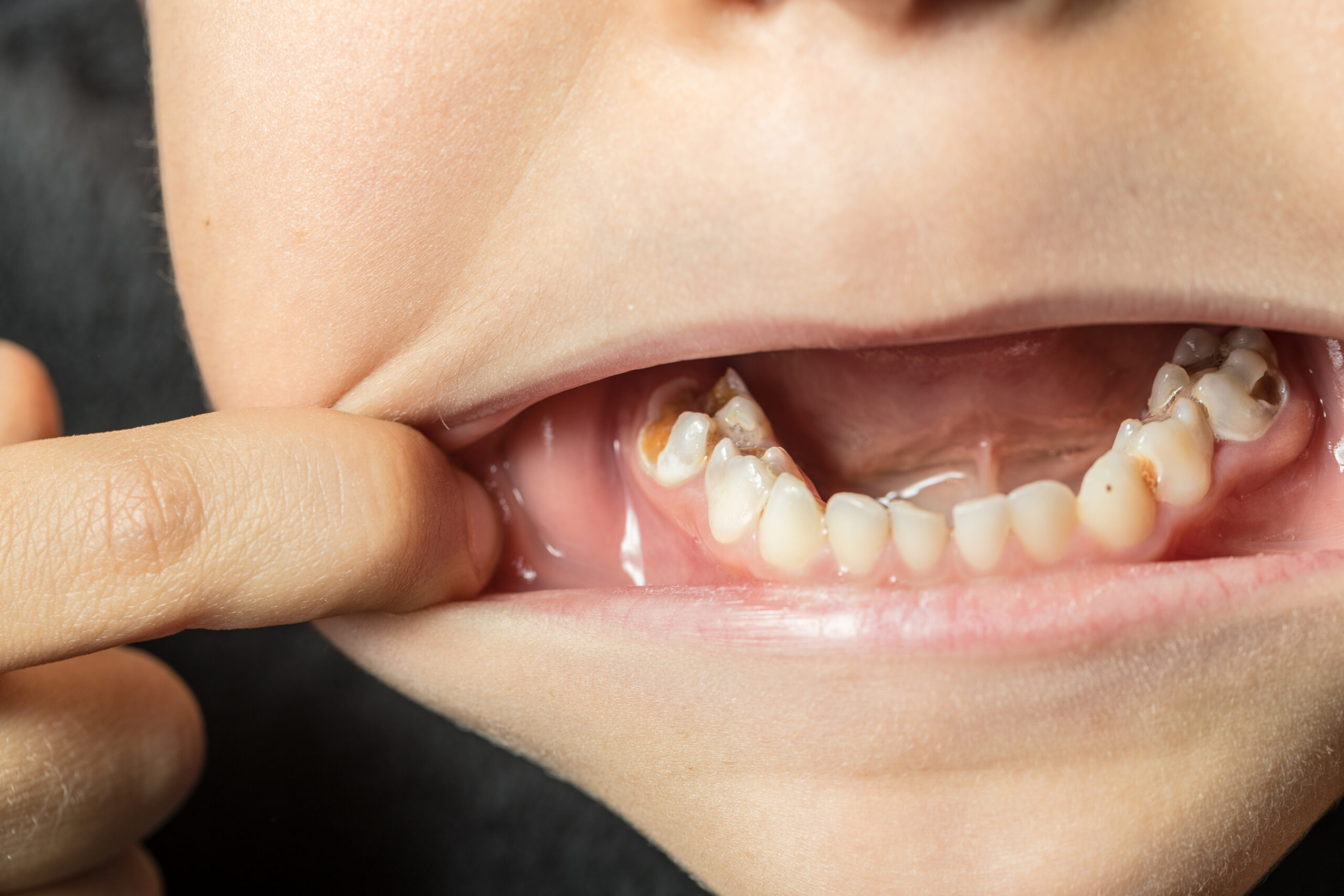
D. Emergency Trauma Management (fractured teeth, luxations)
-
Problem Addressed: Broken or displaced teeth from falls or injuries.

-
How to Check: Visible cracks, bleeding, or a tooth out of place; seek immediate care.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist or Emergency Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Rinse mouth, apply cold compress, and save knocked-out tooth in milk.

-
Milestone: Common between ages 2–10 due to active play.


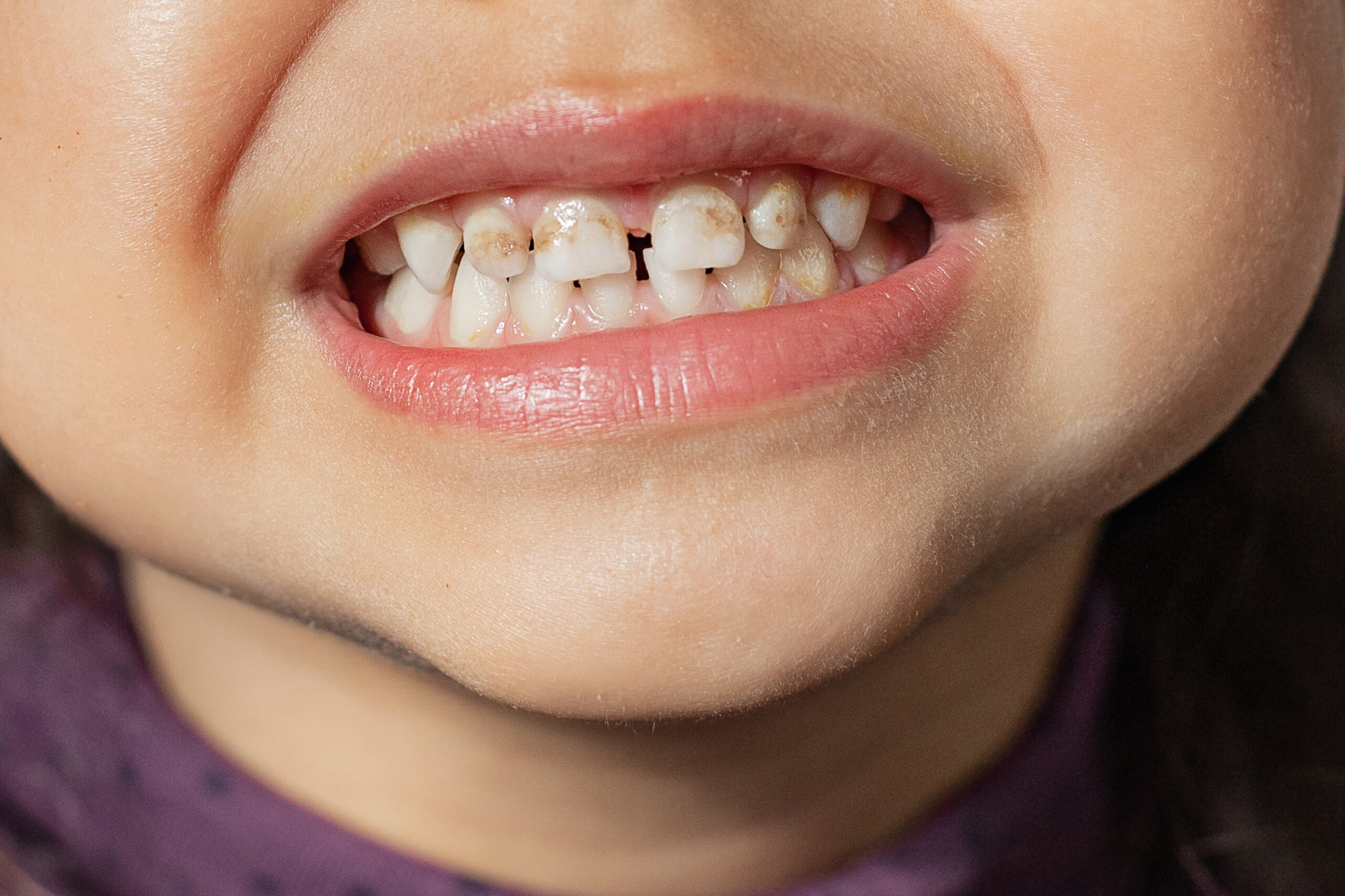
E. Management of Enamel Hypoplasia or MIH (Molar Incisor Hypomineralization)
-
Problem Addressed: Weak or discolored enamel due to developmental issues.

-
How to Check: White/yellow spots or soft enamel; dentist can diagnose.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist.

-
Home Care Tip: Use desensitizing toothpaste if sensitive.

-
Milestone: Appears when permanent teeth erupt (ages 6–8).


F. Sedation/GA for Uncooperative or Special Needs Children
-
Problem Addressed: Anxiety or inability to cooperate during dental work.

-
How to Check: Extreme fear or distress during visits; discuss with dentist.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist with sedation training or Anesthesiologist.

-
Home Care Tip: Practice calming techniques before visits.

-
Milestone: Needed anytime if cooperation is an issue.

G. Tongue Tie/Lip Tie Release (Frenectomy)
-
Problem Addressed: Restricted tongue or lip movement affecting feeding or speech.

-
How to Check: Difficulty lifting tongue or breastfeeding issues; dentist can assess.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist or Oral Surgeon.

-
Home Care Tip: Follow stretching exercises post-procedure.

-
Milestone: Often addressed in infancy or early childhood.

H. Management of Delayed Tooth Eruption or Missing Teeth
-
Problem Addressed: Teeth not appearing on time or absent due to genetics.

-
How to Check: No teeth by age 1 or missing permanent teeth by age 7–8; X-rays needed.

-
Specialist: Pediatric Dentist or Orthodontist.

-
Home Care Tip: Monitor growth and consult regularly.

-
Milestone: Permanent teeth should emerge by age 7.

